RPMsg Design Document
RPMsg is a framework to allow communication between two processors. RPMsg implementation in OpenAMP library is based on virtio. It complies the RPMsg Linux kernel implementation. It defines the handshaking on setting up and tearing down the communication between applications running on two processors.
RPMsg User API Flow Charts
RPMsg Static Endpoint
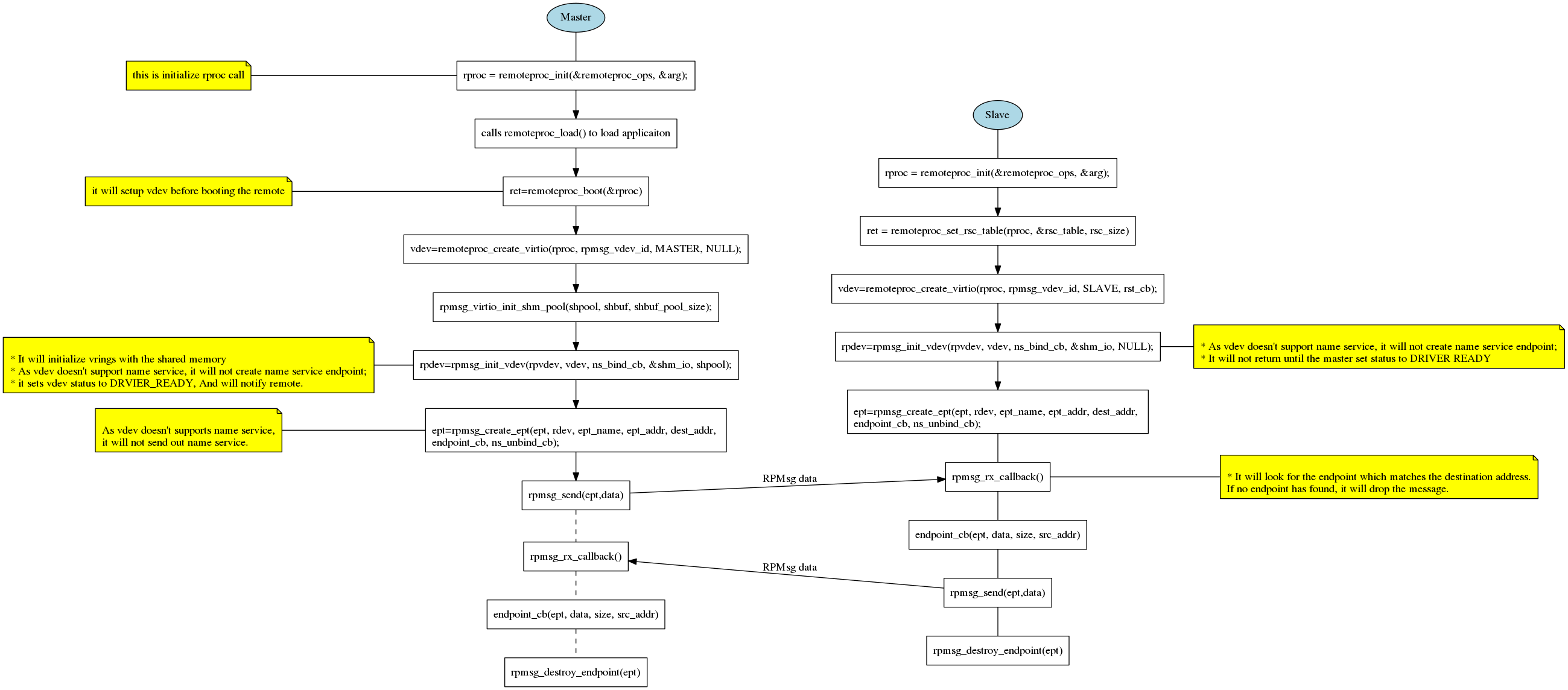
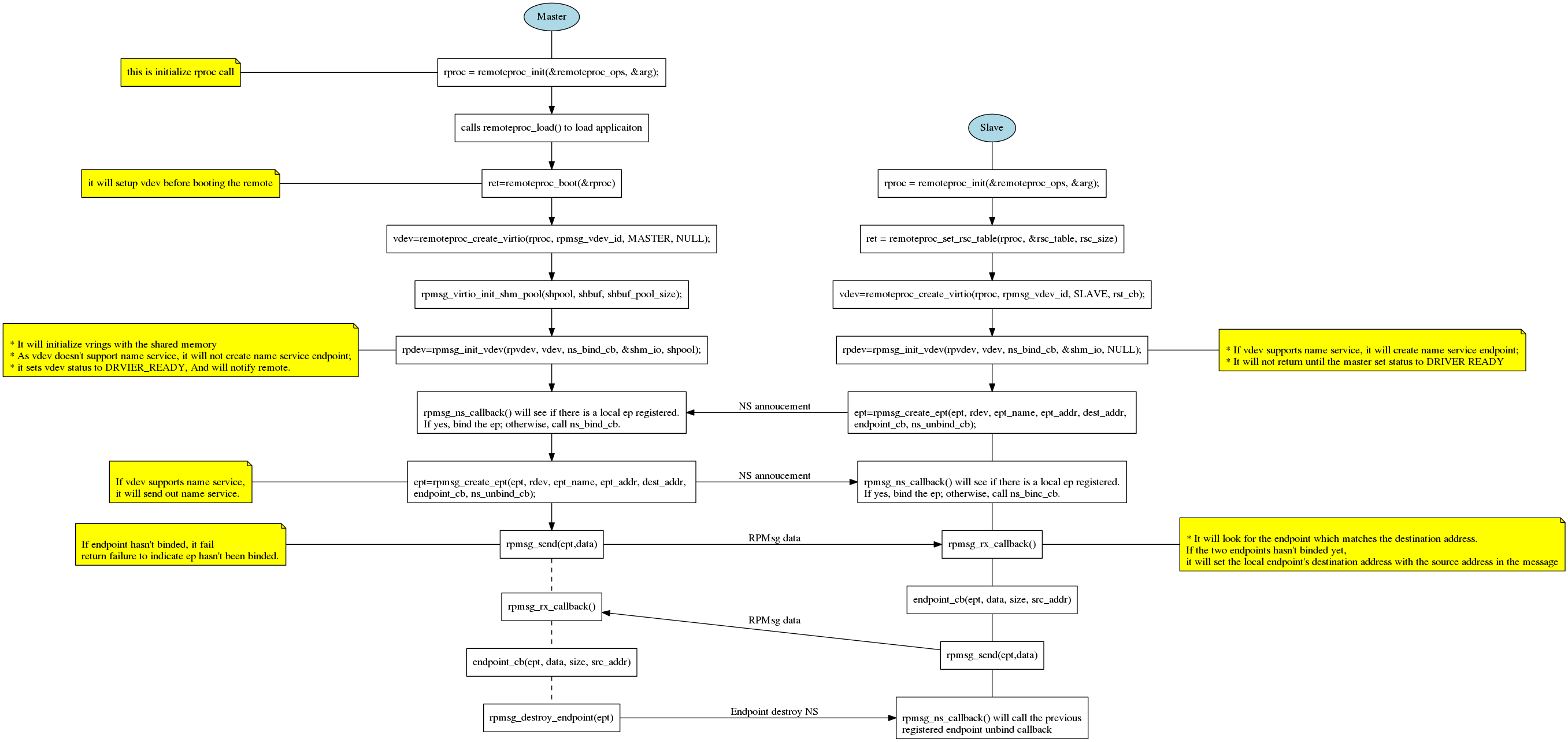
Binding Endpoint Dynamically with Name Service
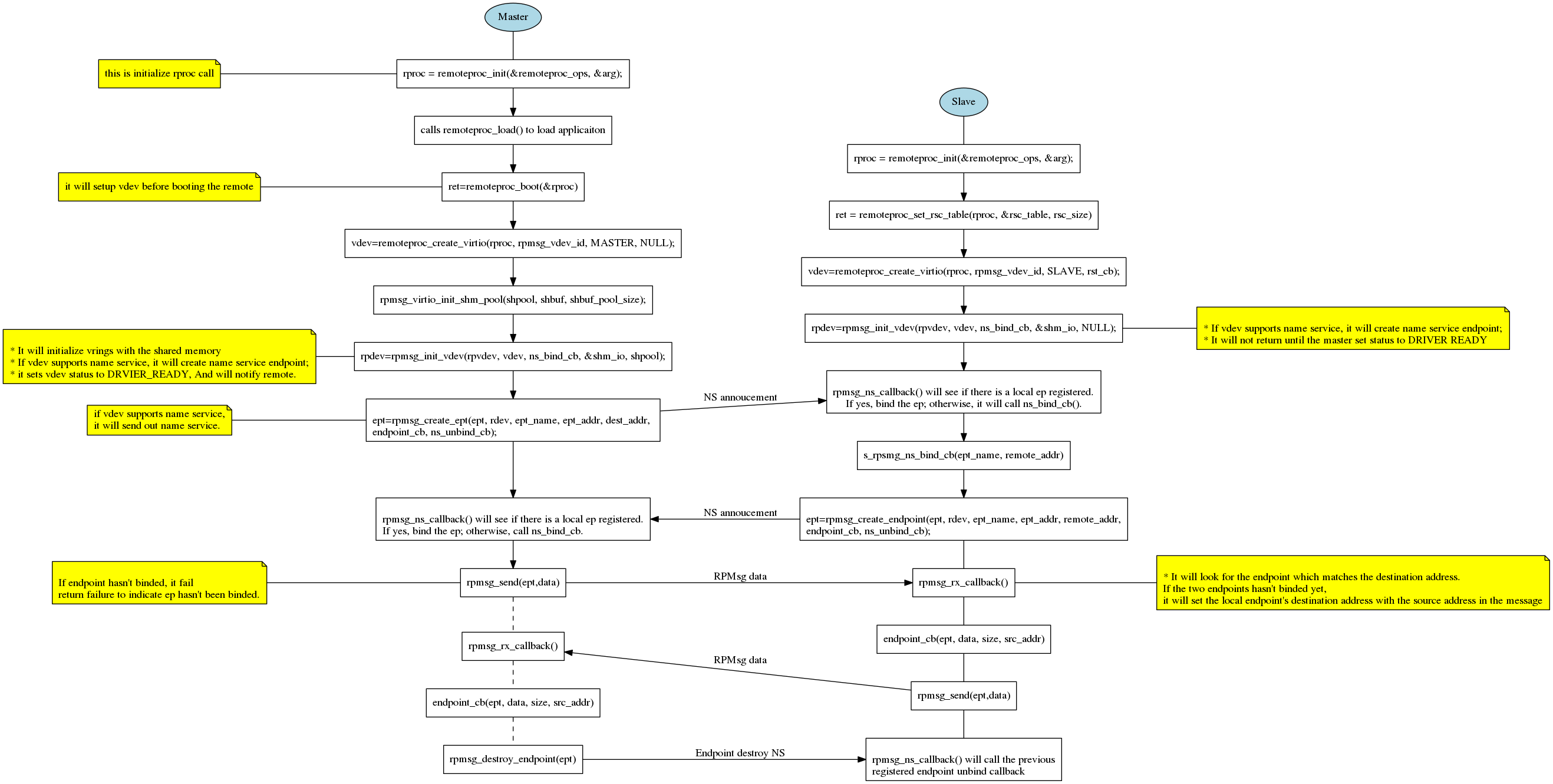
Creating Endpoint Dynamically with Name Service
RPMsg User APIs
-
void rpmsg_virtio_init_shm_pool(struct rpmsg_virtio_shm_pool *shpool, void *shbuf, size_t size)
Initialize default shared buffers pool.
RPMsg virtio has default shared buffers pool implementation. The memory assigned to this pool will be dedicated to the RPMsg virtio. This function has to be called before calling rpmsg_init_vdev, to initialize the rpmsg_virtio_shm_pool structure.
- Parameters:
shpool – Pointer to the shared buffers pool structure
shbuf – Pointer to the beginning of shared buffers
size – Shared buffers total size
-
int rpmsg_init_vdev(struct rpmsg_virtio_device *rvdev, struct virtio_device *vdev, rpmsg_ns_bind_cb ns_bind_cb, struct metal_io_region *shm_io, struct rpmsg_virtio_shm_pool *shpool)
Initialize rpmsg virtio device.
Host side: Initialize RPMsg virtio queues and shared buffers, the address of shm can be ANY. In this case, function will get shared memory from system shared memory pools. If the vdev has the RPMsg name service feature, this API will create a name service endpoint.
Remote side: This API will not return until the driver ready is set by the host side.
- Parameters:
rvdev – Pointer to the rpmsg virtio device
vdev – Pointer to the virtio device
ns_bind_cb – Callback handler for name service announcement without local endpoints waiting to bind.
shm_io – Pointer to the share memory I/O region.
shpool – Pointer to shared memory pool. rpmsg_virtio_init_shm_pool has to be called first to fill this structure.
- Returns:
Status of function execution
-
void rpmsg_deinit_vdev(struct rpmsg_virtio_device *rvdev)
Deinitialize rpmsg virtio device.
- Parameters:
rvdev – Pointer to the rpmsg virtio device
-
static inline struct rpmsg_device *rpmsg_virtio_get_rpmsg_device(struct rpmsg_virtio_device *rvdev)
Get RPMsg device from RPMsg virtio device.
- Parameters:
rvdev – Pointer to RPMsg virtio device
- Returns:
RPMsg device pointed by RPMsg virtio device
RPMsg virtio endpoint APIs
-
int rpmsg_create_ept(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, struct rpmsg_device *rdev, const char *name, uint32_t src, uint32_t dest, rpmsg_ept_cb cb, rpmsg_ns_unbind_cb ns_unbind_cb)
Create rpmsg endpoint and register it to rpmsg device.
Create a RPMsg endpoint, initialize it with a name, source address, remoteproc address, endpoint callback, and destroy endpoint callback, and register it to the RPMsg device.
In essence, an rpmsg endpoint represents a listener on the rpmsg bus, as it binds an rpmsg address with an rx callback handler.
Rpmsg client should create an endpoint to discuss with remote. rpmsg client provide at least a channel name, a callback for message notification and by default endpoint source address should be set to RPMSG_ADDR_ANY.
As an option Some rpmsg clients can specify an endpoint with a specific source address.
- Parameters:
ept – Pointer to rpmsg endpoint
rdev – RPMsg device associated with the endpoint
name – Service name associated to the endpoint (maximum size RPMSG_NAME_SIZE)
src – Local address of the endpoint
dest – Target address of the endpoint
cb – Endpoint callback
ns_unbind_cb – Endpoint service unbind callback, called when remote ept is destroyed.
- Returns:
0 on success, or negative error value on failure.
-
void rpmsg_destroy_ept(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept)
Destroy rpmsg endpoint and unregister it from rpmsg device.
It unregisters the rpmsg endpoint from the rpmsg device and calls the destroy endpoint callback if it is provided.
- Parameters:
ept – Pointer to the rpmsg endpoint
-
static inline unsigned int is_rpmsg_ept_ready(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept)
Check if the rpmsg endpoint ready to send.
- Parameters:
ept – Pointer to rpmsg endpoint
- Returns:
1 if the rpmsg endpoint has both local addr and destination addr set, 0 otherwise
RPMsg messaging APIs
-
static inline int rpmsg_send(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len)
Send a message across to the remote processor.
This function sends
dataof lengthlenbased on theept. The message will be sent to the remote processor which the channel belongs to, usingept’s source and destination addresses. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will block until one becomes available, or a timeout of 15 seconds elapses. When the latter happens, -ERESTARTSYS is returned.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – Payload of the message
len – Length of the payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_sendto(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len, uint32_t dst)
Send a message across to the remote processor, specify dst.
This function sends
dataof lengthlento the remotedstaddress. The message will be sent to the remote processor which theeptchannel belongs to, usingept’s source address. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will block until one becomes available, or a timeout of 15 seconds elapses. When the latter happens, -ERESTARTSYS is returned.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – Payload of message
len – Length of payload
dst – Destination address
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_send_offchannel(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, uint32_t src, uint32_t dst, const void *data, int len)
Send a message using explicit src/dst addresses.
This function sends
dataof lengthlento the remotedstaddress, and usessrcas the source address. The message will be sent to the remote processor which theeptchannel belongs to. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will block until one becomes available, or a timeout of 15 seconds elapses. When the latter happens, -ERESTARTSYS is returned.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
src – Source address
dst – Destination address
data – Payload of message
len – Length of payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_trysend(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len)
Send a message across to the remote processor.
This function sends
dataof lengthlenon theeptchannel. The message will be sent to the remote processor which theeptchannel belongs to, usingept’s source and destination addresses. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will immediately return -ENOMEM without waiting until one becomes available.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – Payload of message
len – Length of payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_trysendto(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len, uint32_t dst)
Send a message across to the remote processor, specify dst.
This function sends
dataof lengthlento the remotedstaddress. The message will be sent to the remote processor which theeptchannel belongs to, usingept’s source address. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will immediately return -ENOMEM without waiting until one becomes available.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – Payload of message
len – Length of payload
dst – Destination address
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_trysend_offchannel(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, uint32_t src, uint32_t dst, const void *data, int len)
Send a message using explicit src/dst addresses.
This function sends
dataof lengthlento the remotedstaddress, and usessrcas the source address. The message will be sent to the remote processor which theeptchannel belongs to. In case there are no TX buffers available, the function will immediately return -ENOMEM without waiting until one becomes available.- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
src – Source address
dst – Destination address
data – Payload of message
len – Length of payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
void rpmsg_hold_rx_buffer(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, void *rxbuf)
Holds the rx buffer for usage outside the receive callback.
Calling this function prevents the RPMsg receive buffer from being released back to the pool of shmem buffers. This API can only be called at rx callback context (rpmsg_rx_cb_t). With this API, the application doesn’t need to copy the message in rx callback. Instead, the rx buffer base address is saved in application context and further processed in application process. After the message is processed, the application can release the rx buffer for future reuse in vring by calling the rpmsg_release_rx_buffer() function.
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
rxbuf – RX buffer with message payload
-
void rpmsg_release_rx_buffer(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, void *rxbuf)
Releases the rx buffer for future reuse in vring.
This API can be called at process context when the message in rx buffer is processed.
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
rxbuf – rx buffer with message payload
-
void *rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, uint32_t *len, int wait)
Gets the tx buffer for message payload.
This API can only be called at process context to get the tx buffer in vring. By this way, the application can directly put its message into the vring tx buffer without copy from an application buffer. It is the application responsibility to correctly fill the allocated tx buffer by data and passing correct parameters to the rpmsg_send_nocopy() or rpmsg_sendto_nocopy() function to perform data no-copy-send mechanism.
See also
See also
See also
- Parameters:
ept – Pointer to rpmsg endpoint
len – Pointer to store tx buffer size
wait – Boolean, wait or not for buffer to become available
- Returns:
The tx buffer address on success and NULL on failure
-
static inline int rpmsg_send_nocopy(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len)
Send a message in tx buffer reserved by rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() across to the remote processor.
This function sends buf of length len on the ept endpoint. The message will be sent to the remote processor which the ept endpoint belongs to, using ept’s source and destination addresses. The application has to take the responsibility for:
tx buffer reserved (rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() )
filling the data to be sent into the pre-allocated tx buffer
not exceeding the buffer size when filling the data
data cache coherency
After the rpmsg_send_nocopy() function is issued the tx buffer is no more owned by the sending task and must not be touched anymore unless the rpmsg_send_nocopy() function fails and returns an error. In that case the application should try to re-issue the rpmsg_send_nocopy() again.
See also
See also
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – TX buffer with message filled
len – Length of payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
static inline int rpmsg_sendto_nocopy(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, const void *data, int len, uint32_t dst)
Sends a message in tx buffer allocated by rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() across to the remote processor, specify dst.
This function sends buf of length len to the remote dst address. The message will be sent to the remote processor which the ept endpoint belongs to, using ept’s source address. The application has to take the responsibility for:
tx buffer allocation (rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() )
filling the data to be sent into the pre-allocated tx buffer
not exceeding the buffer size when filling the data
data cache coherency
After the rpmsg_sendto_nocopy() function is issued the tx buffer is no more owned by the sending task and must not be touched anymore unless the rpmsg_sendto_nocopy() function fails and returns an error. In that case the application should try to re-issue the rpmsg_sendto_nocopy() again.
See also
See also
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
data – TX buffer with message filled
len – Length of payload
dst – Destination address
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
int rpmsg_send_offchannel_nocopy(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, uint32_t src, uint32_t dst, const void *data, int len)
Send a message in tx buffer reserved by rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() across to the remote processor.
This function sends buf of length len to the remote dst address, and uses src as the source address. The message will be sent to the remote processor which the ept endpoint belongs to. The application has to take the responsibility for:
tx buffer reserved (rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer() )
filling the data to be sent into the pre-allocated tx buffer
not exceeding the buffer size when filling the data
data cache coherency
After the rpmsg_send_offchannel_nocopy() function is issued the tx buffer is no more owned by the sending task and must not be touched anymore unless the rpmsg_send_offchannel_nocopy() function fails and returns an error. In that case application should try to re-issue the rpmsg_send_offchannel_nocopy() again.
See also
See also
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
src – The rpmsg endpoint local address
dst – The rpmsg endpoint remote address
data – TX buffer with message filled
len – Length of payload
- Returns:
Number of bytes it has sent or negative error value on failure.
-
int rpmsg_release_tx_buffer(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, void *txbuf)
Releases unused buffer.
This API can be called when the Tx buffer reserved by rpmsg_get_tx_payload_buffer needs to be released without having been sent to the remote side.
Note that the rpmsg virtio is not able to detect if a buffer has already been released. The user must prevent a double release (e.g. by resetting its buffer pointer to zero after the release).
See also
- Parameters:
ept – The rpmsg endpoint
txbuf – tx buffer with message payload
- Returns:
RPMSG_SUCCESS on success
RPMSG_ERR_PARAM on invalid parameter
RPMSG_ERR_PERM if service not implemented
RPMsg User Defined Callbacks
RPMsg endpoint message received callback:
-
typedef int (*rpmsg_ept_cb)(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept, void *data, size_t len, uint32_t src, void *priv)
RPMsg name service binding callback. If user defines such callback, when there is a name service announcement arrives, if there is no registered endpoint found to bind to this name service, it will call this callback. If this callback is not defined, it will drop this name service.:
-
typedef void (*rpmsg_ns_bind_cb)(struct rpmsg_device *rdev, const char *name, uint32_t dest)
RPMsg name service unbind callback. If user defines such callback, when there is name service destroy arrives, it will call this callback.:
-
typedef void (*rpmsg_ns_unbind_cb)(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept)
RPMsg endpoint name service unbind callback. If user defines such callback, when there is name service destroy arrives, it will call this callback to notify the user application about the remote has destroyed the service.:
-
typedef void (*rpmsg_ns_unbind_cb)(struct rpmsg_endpoint *ept)